Flow measurement is an essential task in many industries, including chemical, pharmaceutical, water treatment, and food and beverage. Accurate flow measurement ensures proper control over processes and guarantees efficiency, safety, and compliance with regulations. There are various types of flow meters available, and one of the most reliable and accurate types is the rotary piston flowmeter. But what exactly are rotary piston flowmeters, and how do they function? This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of rotary piston flowmeters, their working principles, applications, and key advantages.
What is a Rotary Piston Flowmeter?
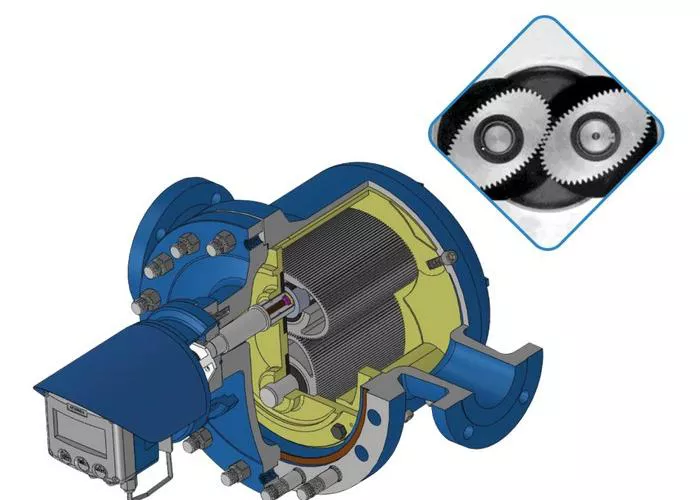
A rotary piston flowmeter is a type of positive displacement flowmeter. It measures the flow rate of a fluid by counting the number of times a piston moves through a chamber as the fluid passes through it. The movement of the piston is directly proportional to the volume of fluid flowing through the meter. This type of flowmeter is often used for applications that require high accuracy in measuring low to medium flow rates of clean, low-viscosity liquids and gases.
Rotary piston flowmeters are known for their durability, accuracy, and reliability, especially in challenging environments. They operate by capturing a precise volume of fluid within a sealed chamber and then measuring how many times the piston rotates as fluid flows through the meter.
How Does a Rotary Piston Flowmeter Work?
The operation of a rotary piston flowmeter is based on a straightforward mechanical process that ensures accuracy and precision. To understand this process more clearly, let’s break down the working principle into a few steps:
1. Fluid Enters the Flowmeter
When a fluid enters the flowmeter, it enters a chamber that contains a piston. The piston is positioned in such a way that it is free to rotate within the chamber as the fluid flows past it. The fluid is directed through a narrow inlet, which ensures a controlled flow of the fluid and prevents air bubbles or turbulence, which could affect measurement accuracy.
2. The Piston Movement
As the fluid enters the chamber, it pushes against the piston, causing it to rotate. The piston has an eccentric shape, often designed to fit the specific type of fluid being measured. The flowmeter is calibrated so that each rotation of the piston corresponds to a fixed volume of fluid, ensuring accurate measurement.
3. Counting Piston Revolutions
As the fluid continues to flow through the meter, the piston rotates repeatedly. Each full rotation of the piston corresponds to the measurement of a specific volume of fluid that has passed through the flowmeter. The number of revolutions can be tracked by mechanical or electronic counters connected to the meter. This information is then used to calculate the flow rate.
4. Output Signals
The revolutions of the piston are typically transmitted to an electronic register or counter, which calculates the total volume of fluid passing through the meter. Depending on the flowmeter design, the output can be in the form of mechanical dials, digital displays, or even signals sent to a control system for integration with process control systems.
5. Resetting the Measurement
In most cases, after each reading or during periodic maintenance, the flowmeter’s counter can be reset to zero. This allows operators to track the flow over a specific period or reset the device for future measurements.
Key Components of Rotary Piston Flowmeters
To better understand how rotary piston flowmeters work, it’s essential to recognize the key components that make up these devices. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring that the meter functions correctly and accurately measures the flow of fluids:
1. Piston
The piston is the primary moving part of the rotary piston flowmeter. It is designed to rotate within the flowmeter’s chamber as fluid passes through it. The piston is typically made from high-quality, durable materials like stainless steel, ceramic, or specialized plastics, depending on the type of fluid being measured and the required durability.
2. Chamber
The chamber houses the piston and guides its movement. It is carefully designed to ensure minimal friction while maintaining a tight seal around the piston. This precision is crucial for the accuracy of the flow measurement, as even small deviations can lead to incorrect readings.
3. Bearings
Bearings are used to support the piston and allow it to rotate smoothly within the chamber. These bearings help reduce friction and wear, which improves the longevity and reliability of the flowmeter.
4. Shaft and Gear Mechanism
The shaft and gear mechanism transmit the rotational movement of the piston to a counter or digital register. These mechanical parts ensure that every revolution of the piston is recorded accurately and consistently.
5. Seals and Gaskets
Seals and gaskets are critical for ensuring that the chamber remains airtight, preventing leaks of the fluid being measured. High-quality seals are essential to maintain the accuracy of measurements and to prevent contamination of the fluid.
Types of Rotary Piston Flowmeters
While rotary piston flowmeters generally operate on the same basic principle, different types of flowmeters are designed to suit specific applications or fluids. These variations are primarily determined by the design of the piston, the materials used, and the way the meter measures the flow rate. Below are the main types of rotary piston flowmeters:
1. Positive Displacement Flowmeters
Positive displacement rotary piston flowmeters are the most common type. They measure the exact volume of fluid passing through the meter by counting the number of revolutions of the piston. This type is ideal for highly accurate flow measurements, especially in low- to medium-flow applications, and for fluids with consistent viscosity.
2. Liquid Flowmeters
Rotary piston flowmeters are commonly used for measuring the flow of liquids in industries such as water treatment, food processing, and chemicals. Liquid flowmeters are designed to handle low-viscosity liquids, where the volume of liquid passing through the meter is directly proportional to the number of piston revolutions.
3. Gas Flowmeters
Rotary piston flowmeters are also used for measuring the flow of gases. However, gas flow measurement can be more complex than liquid flow due to the compressibility of gases. The design of the flowmeter and the piston may vary to account for factors such as pressure and temperature, which can affect the gas’s density and volume.
Applications of Rotary Piston Flowmeters
Rotary piston flowmeters are versatile devices that are widely used in various industries. Some of the primary applications include:
1. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industry
In the chemical and pharmaceutical industries, rotary piston flowmeters are often used for the precise measurement of chemicals, solvents, and other reactive substances. These industries require high accuracy to ensure product quality and adherence to strict regulatory standards.
2. Water and Wastewater Treatment
Water and wastewater treatment plants utilize rotary piston flowmeters to measure the flow of water, chemicals, and other liquids throughout the treatment process. Accurate flow measurement is crucial for controlling chemical dosages, maintaining proper flow rates, and ensuring optimal operation of treatment systems.
3. Food and Beverage Industry
In food and beverage manufacturing, rotary piston flowmeters are employed to measure the flow of ingredients such as oils, syrups, and other liquids. These meters help ensure consistency in product formulation, maintaining quality and taste across batches.
4. Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry uses rotary piston flowmeters for measuring fuel flow, lubricants, and gases in pipelines and machinery. Accurate flow measurement in these industries is crucial for optimizing production rates, improving safety, and ensuring proper distribution of resources.
Advantages of Rotary Piston Flowmeters
Rotary piston flowmeters offer several advantages that make them ideal for use in many applications:
1. High Accuracy
Rotary piston flowmeters are highly accurate because they measure the exact volume of fluid passing through the meter by counting the number of piston revolutions. This makes them ideal for applications where precise measurements are essential.
2. Durability
These flowmeters are built to withstand harsh operating conditions, including high pressure, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to corrosive fluids. Their durable construction ensures a long lifespan, even in challenging environments.
3. Low Maintenance
Rotary piston flowmeters require minimal maintenance due to their simple mechanical design. The key moving parts are generally designed for extended life, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
4. Versatility
Rotary piston flowmeters can measure a wide range of fluids, including liquids and gases. This versatility makes them suitable for use in many different industries and applications.
Challenges and Considerations
While rotary piston flowmeters are reliable and accurate, there are a few challenges and considerations to keep in mind when selecting and using them:
1. Viscosity Limitations
Rotary piston flowmeters are most effective for low-viscosity fluids. High-viscosity fluids can cause the piston to move more slowly or get stuck, which can lead to inaccurate measurements. For high-viscosity fluids, alternative types of flowmeters, such as gear or electromagnetic meters, may be more appropriate.
2. Gas Flow Measurement
Measuring gas flow with rotary piston flowmeters requires careful attention to factors such as pressure and temperature. Without proper calibration, these factors can introduce measurement errors.
Conclusion
Rotary piston flowmeters are highly accurate and reliable devices commonly used to measure the flow of liquids and gases in various industries. Their operation, based on positive displacement and piston movement, ensures precise measurements of fluid volumes. These flowmeters are ideal for applications that require consistent, low- to medium-flow measurements of clean, low-viscosity fluids. While rotary piston flowmeters offer many benefits, it’s important to consider factors such as viscosity and gas flow dynamics when selecting the appropriate flowmeter for specific applications. By understanding the principles, components, and applications of rotary piston flowmeters, businesses can improve the efficiency, accuracy, and safety of their operations.