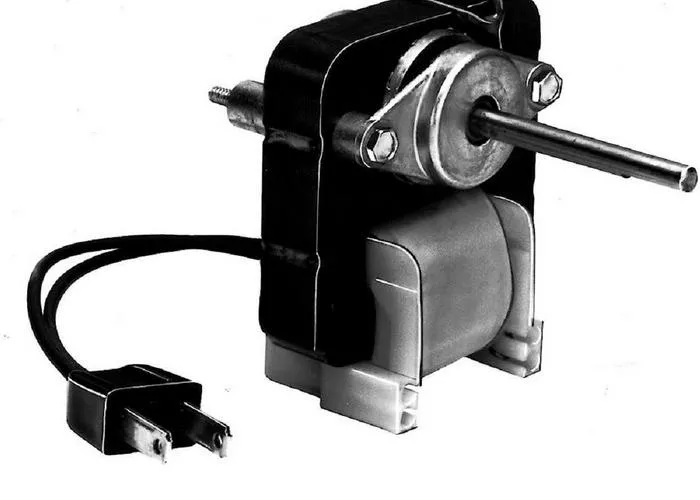
The C-Frame shaded pole motor is a compact, low-torque electric motor designed for light-duty applications. This type of motor is widely recognized for its simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Frequently found in small appliances and low-power devices, the C-Frame shaded pole motor plays a crucial role in the operation of household fans, hairdryers, microwave ovens, and HVAC dampers.
The motor derives its name from the shape of its frame, which resembles the letter “C” when viewed from the side. This distinctive open-frame design allows for easy mounting and cooling, making it ideal for appliances with space constraints. The shaded pole motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction and is a subclass of induction motors.
Construction of a C-Frame Shaded Pole Motor
The construction of a C-Frame shaded pole motor is relatively simple, which contributes to its durability and affordability. The primary components include:
- Stator Core: Typically made of laminated silicon steel, the stator is shaped into a ‘C’ form. It serves as the stationary part of the motor and houses the winding and shading coils.
- Main Winding: Positioned within the stator slots, this winding is energized by an AC supply and generates the magnetic field necessary for motor operation.
- Shading Coil (Shaded Pole): A copper ring or short-circuited coil that creates a delayed magnetic field to start rotation. This shaded area of the stator pole helps initiate directional motion.
- Rotor: Usually a squirrel cage rotor, it consists of aluminum bars shorted at the ends by end rings. The rotor is placed within the magnetic field created by the stator.
- Shaft and Bearings: The rotor is mounted on a shaft supported by sleeve or ball bearings, allowing smooth rotation.
Despite their simple construction, C-Frame shaded pole motors can vary in size and power ratings, depending on their application. Their compact design makes them an attractive choice for integration into various electrical equipment.
How Does C-Frame Shaded Pole Motor Work
The operating principle of a C-Frame shaded pole motor relies on the generation of a rotating magnetic field through a shaded pole. When alternating current flows through the main winding, it induces a magnetic flux in the stator core. A portion of this core is surrounded by the shading coil.
As AC flows, the magnetic field strength fluctuates. The shaded portion of the pole causes a phase delay due to the induced current in the copper shading coil. This results in a secondary, lagging magnetic field. The interaction of the main and lagging fields creates a weak rotating magnetic field across the pole face, sufficient to initiate rotor motion.
Once the rotor starts turning, it continues to rotate due to the principles of electromagnetic induction, just like any other motors. However, due to the simplicity of the shaded pole design, the starting torque is relatively low, making it suitable only for low-inertia applications.
Applications of C-Frame Shaded Pole Motors
Given their limited torque and efficiency, C-Frame shaded pole motors are not suitable for heavy-duty tasks. However, they excel in small, continuous-running appliances. Common applications include:
- Refrigerator evaporator and condenser fans
- Range hood blowers
- Bathroom exhaust fans
- Microwave turntables
- Humidifiers and air purifiers
- Clock mechanisms
- HVAC dampers and small actuators
These motors are also preferred in devices where quiet operation and low maintenance are desired. Since they typically operate at lower speeds and loads, their noise levels and wear-and-tear remain minimal over time.
Advantages of C-Frame Shaded Pole Motors
- Simplicity: Fewer components and no brushes or commutators reduce complexity and failure rates.
- Low Cost: The absence of auxiliary windings or capacitors makes them inexpensive to manufacture and maintain.
- Compact Design: Their small footprint allows them to fit easily into constrained spaces.
- Reliability: With fewer moving parts, the motor tends to have a long operational life under proper conditions.
- Continuous Duty: Capable of operating for long periods without overheating when correctly rated.
Limitations of C-Frame Shaded Pole Motors
Despite their many benefits, C-Frame shaded pole motors are not without drawbacks:
- Low Efficiency: The presence of shading coils and a weak rotating field result in poor energy conversion rates.
- Low Starting Torque: Unsuitable for applications that require overcoming high inertia loads.
- Overheating Risk: Prolonged operation under load may lead to thermal issues without proper ventilation.
- Unidirectional: These motors rotate in a single direction unless specifically modified.
In comparison with other single-phase motor types like the split-phase motor or the capacitor-start induction motor, C-Frame shaded pole motors are less versatile but offer greater ease of use in low-load applications.
Comparison with Other Motor Types
To better understand the placement of C-Frame shaded pole motors within the broader motor landscape, it’s helpful to compare them with other commonly used types:
- Squirrel Cage Induction Motor: These motors provide higher efficiency and are suitable for industrial-grade applications, but require more complex control systems.
- Single-Phase Induction Motor: More powerful and often equipped with starting capacitors, they serve a wider range of applications.
- Synchronous Motors: Unlike shaded pole motors, these maintain constant speed irrespective of load.
C-Frame shaded pole motors excel where simplicity, low cost, and compact size matter more than performance or efficiency. They fill a niche that other motors cannot economically serve.
Design Improvements and Modern Innovations
Over time, manufacturers have introduced innovations to improve the performance of C-Frame shaded pole motors. Some models now include dual-speed capabilities, thermally protected windings, or enhanced rotor balancing to reduce vibrations. Innovations in materials, such as high-efficiency laminations and better winding insulation, also contribute to improved durability and slightly better efficiency.
Although still considered low-tech compared to electronically commutated or brushless DC motors, shaded pole motors remain relevant in applications that demand minimal performance and maximum simplicity.
Maintenance and Lifespan
C-Frame shaded pole motors require very little maintenance. Most issues arise due to dust accumulation, bearing wear, or coil overheating. Regular cleaning and occasional lubrication (if applicable) can prolong motor life significantly. In sealed models, maintenance is practically zero.
Typical lifespan ranges between 5,000 to 15,000 operating hours depending on usage conditions. Operating the motor within its rated parameters ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Conclusion
The C-Frame shaded pole motor is a marvel of minimalism in electric motor design. Despite its inherent limitations in torque and efficiency, it continues to be an indispensable component in various domestic and commercial appliances. Its cost-effectiveness, ease of integration, and near-zero maintenance make it the preferred solution in many low-power, continuous-duty scenarios.
Understanding how these motors work and where they fit in the spectrum of motor technology can help engineers and technicians select the appropriate motor for any given application. While it may not compete with advanced motor types in terms of performance, the C-Frame shaded pole motor stands out as a pragmatic choice in specific use-cases that demand economy and simplicity.
FAQs
Q1: Why is it called a shaded pole motor?
A shaded pole motor gets its name from the copper shading coil that wraps around a portion of the stator pole. This “shaded” area creates a lagging magnetic field that helps start the rotor rotation.
Q2: What is the main disadvantage of a C-Frame shaded pole motor?
The main disadvantage is its low efficiency and starting torque, making it unsuitable for high-load or variable-load applications.
Q3: Can a C-Frame shaded pole motor run in both directions?
By default, these motors are unidirectional. However, direction can be reversed by changing the position of the shading coil, which is often impractical and not intended for dynamic applications.
Q4: What type of load is ideal for shaded pole motors?
Shaded pole motors are best suited for low-inertia, continuous loads such as fans, blowers, and small pumps where high starting torque is not required.
Q5: Are shaded pole motors obsolete?
No. While more advanced motor types exist, shaded pole motors remain relevant due to their simplicity, low cost, and reliability in suitable applications.